Albis Plastic 开发用于燃料电池应用的化合物
这些化合物目前正在与多家原始设备制造商合作进行验证。
克莱尔·戈德斯伯里| 2019 年 12 月 3 日
Albis Plastic(德国汉堡)宣布开发用于燃料电池应用的塑料解决方案,目前正在与知名 OEM 的项目中进行验证。验证过程包括 Albis 的技术化合物 Altech、Alfater SL TPV、Tedur L PPS 和 Alcom,所有这些都可以适应客户的特定要求。
电池动力汽车目前正在大规模推向市场,如大众 ID、奥迪 e-tron、宝马 i3、欧宝 Ampera-e 和梅赛德斯 EQC 车型。Albis 表示,毫无疑问,驾驶这些车辆时可以减少 CO 2排放,前提是能源来自可再生能源。
然而,该技术带来了许多需要解决的挑战,该公司补充说,包括资源的采购、每次装载的最大范围以及相关的装载时间。
|
|
|
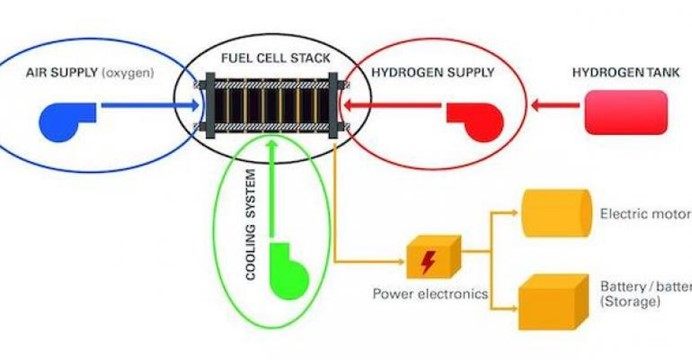
燃料电池系统需要在燃料电池核心本身以及氢气、氧气、空气供应和冷却回路中使用多种材料,包括金属、塑料和密封材料。 图片由 Albis Plastic 提供。 |
"结合电池和燃料电池的混合解决方案在这里是一个很有前途的解决方案,"Albis 管理委员会成员兼复合业务负责人 Ian Mills 说。
燃料电池系统需要使用多种材料,包括金属、塑料和密封材料。它们既用于燃料电池核心本身,即所谓的"堆",也用于氢气、氧气、空气供应和冷却回路。它们还用于泵、阀门、压缩机、管道和连接器等部件。
诸如挥发性成分或离子之类的污染物会通过排放导致燃料电池的退化,从而通过改变"双极板"的表面等方式降低其使用寿命和性能。这些挥发性成分可以从燃料电池的各个组件中使用的材料中迁移出来。
"由于有大量单独的零件和附件,几乎不可能用完全零排放的组件生产燃料电池系统,"汽车业务开发经理 Thies Wrobel 解释说。"因此,必须仔细检查所用材料的排放量。"
另一个重要因素是在清洁的生产环境中使用相同的原材料以一致、可重复的工艺生产材料。考虑到这些因素并与 OEM 合作,Albis 开发了已在冷却和供气系统中进行测试的材料。
这些材料包括来自 Altech PP 产品组合的聚丙烯化合物,其中含有 20%、40% 和 50% 的玻璃纤维;Tedur L 产品组合中的 PPS 化合物,含有 30% 和 40% 的玻璃纤维以及 15% 的 PTE(用于轴承应用);和 Alfater TPV,一种过氧化交联的热塑性硫化橡胶,具有与弹性体/橡胶相媲美的肖氏 A 60 和 70 硬度(用于密封应用)。
未来,Albis 实验室将在专门安装的测试台上测试其他化合物。
Albis Plastic develops compounds for fuel-cell applications
The compounds are currently being validated in collaboration with several OEMs.
Clare Goldsberry | Dec 03, 2019
Albis Plastic (Hamburg, Germany) announced the development of a plastic solution for fuel-cell applications, which is currently being validated in projects with well-known OEMs. The validation process includes Albis' technical compounds Altech, Alfater SL TPV, Tedur L PPS and Alcom, all of which can be adapted to customer-specific requirements.
Battery-powered cars are currently being introduced to the market on a large scale, such as the VW ID, Audi e-tron, BMW i3, Opel Ampera-e and Mercedes EQC models. Albis stated that it has no doubt that CO2 emissions can be reduced while driving these vehicles, provided the energy comes from renewable sources.
However, this technology poses a number of challenges that need to be addressed, added the company, including the procurement of resources, the maximum range per load and the associated duration of loading times.
|
|
|
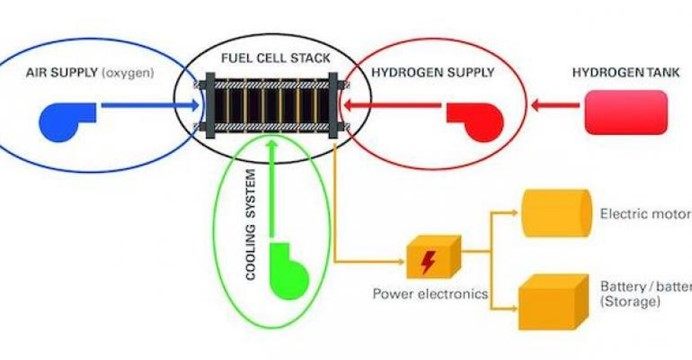
Fuel-cell systems require the use of numerous materials, including metals, plastics and sealing materials, in the fuel-cell core itself as well as the hydrogen, oxygen, air supply and cooling circuit. Image courtesy Albis Plastic. |
"Hybrid solutions that combine battery and fuel cells are a promising solution here," said Ian Mills, a member of the Albis Management Board and head of the Compounding business.
Fuel-cell systems require the use of numerous materials, including metals, plastics and sealing materials. These are used both for the fuel cell core itself, the so-called "stack," and the hydrogen, oxygen, air supply and cooling circuit. They are also used in components such as pumps, valves, compressors, pipes and connectors.
Pollutants, such as volatile components or ions, can contribute to the degradation of the fuel cell through emissions and, thus, reduce its service life and performance by changing the surfaces of the "bipolar plates," for example. These volatile components can migrate from the materials used in the individual assemblies of the fuel cell.
"The production of a fuel-cell system from completely emission-free components is almost impossible because of the large number of individual parts and attachments," explained Thies Wrobel, Business Development Manager—Automotive. "Therefore, the materials used must be carefully examined for emissions."
Another important factor is production of the materials in a consistent, reproducible process using the same raw materials in a clean production environment. Given these considerations and in cooperation with OEMs, Albis has developed materials that have been tested in cooling and air supply systems.
The materials include polypropylene compounds from the Altech PP portfolio with 20%, 40% and 50% glass fibers; PPS compounds from the Tedur L portfolio with 30% and 40% glass fibers plus 15% PTE (for bearing applications); and Alfater TPV, a peroxidically cross-linked thermoplastic vulcanizate with comparable properties to elastomer/rubber in Shore A 60 and 70 hardness (for sealing applications).
Additional compounds will be tested in the future at Albis' laboratory on a specially installed test rig.
 艾邦氢能产业链通讯录,目前有2200人加入,如亿华通、清极能源、氢蓝时代、雄韬、氢牛、氢璞、爱德曼、氢晨、喜马拉雅、明天氢能、康明斯、新源动力、巴拉德、现代汽车、神力科技、中船712等等,可以按照标签筛选,请点击下方关键词试试
资料下载:
艾邦氢能产业链通讯录,目前有2200人加入,如亿华通、清极能源、氢蓝时代、雄韬、氢牛、氢璞、爱德曼、氢晨、喜马拉雅、明天氢能、康明斯、新源动力、巴拉德、现代汽车、神力科技、中船712等等,可以按照标签筛选,请点击下方关键词试试
资料下载:



